Bipolar depression is a complex and challenging aspect of bipolar disorder that requires specialized care. At Alice’s Psychiatry and Wellness, we understand the importance of following evidence-based treatment bipolar depression guidelines to provide the best possible outcomes for our patients.
This blog post will explore the key strategies for managing bipolar depression, including medication options, psychosocial interventions, and the critical role of personalized treatment plans.
What Is Bipolar Depression?
Understanding Bipolar Depression
Bipolar depression forms a complex and often misunderstood aspect of bipolar disorder. This condition involves debilitating and long-lasting depressive episodes, distinct from the manic or hypomanic episodes that characterize bipolar disorder.
Recognizing Bipolar Depression
Bipolar depression shares many symptoms with unipolar depression, including persistent sadness, loss of interest in activities, changes in appetite and sleep patterns, and difficulty concentrating. However, subtle differences can help identify bipolar depression:
- Increased sleep: People with bipolar depression often experience hypersomnia, sleeping for extended periods.
- Cognitive symptoms: Bipolar depression frequently involves more severe cognitive impairment, including difficulty making decisions and slower thought processes.
- Psychomotor changes: Many individuals with bipolar depression experience physical slowing or agitation that others notice.
Distinguishing Bipolar from Unipolar Depression
One of the most significant challenges in treating bipolar depression involves distinguishing it from unipolar depression. The National Institute of Mental Health reports that many individuals with bipolar disorder receive an initial misdiagnosis of major depressive disorder, leading to inappropriate treatment.
Key differences include:
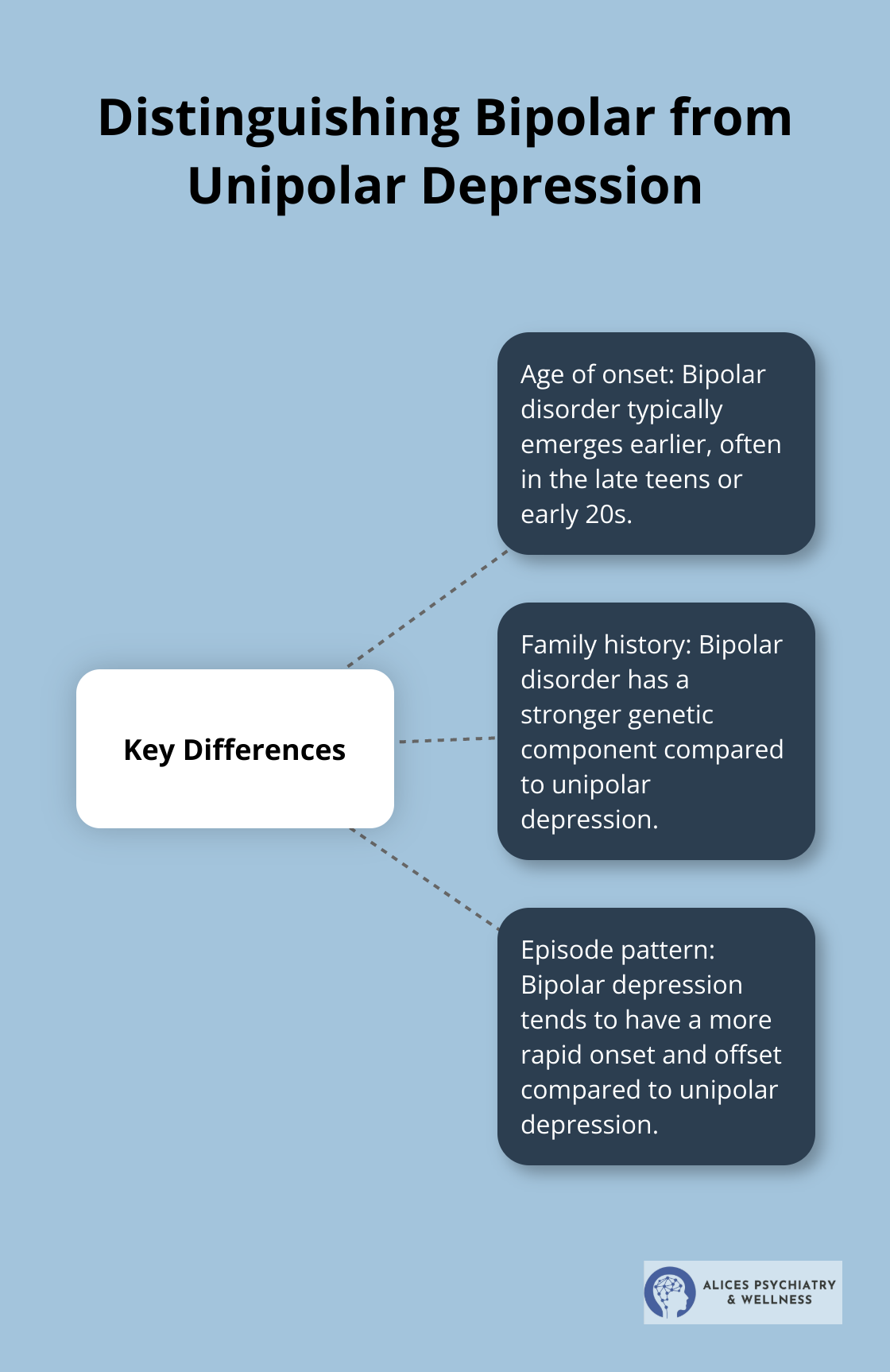
- Age of onset: Bipolar disorder typically emerges earlier (often in the late teens or early 20s).
- Family history: Bipolar disorder has a stronger genetic component.
- Episode pattern: Bipolar depression tends to have a more rapid onset and offset compared to unipolar depression.
The Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis proves essential for effective treatment. Early, accurate diagnosis can substantially reduce the burden of bipolar disorder and improve the long-term outcome for patients. Misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective treatment strategies or even worsen symptoms. For instance, antidepressants (commonly used for unipolar depression) can trigger manic episodes in individuals with bipolar disorder if not carefully managed.
Comprehensive evaluation techniques, including detailed patient histories and advanced screening tools, ensure accurate diagnosis. This approach allows for the development of tailored treatment plans that address the unique needs of each individual with bipolar depression.
Moving Forward with Treatment
With a clear understanding of bipolar depression and its unique characteristics, the next step involves exploring effective treatment options. Medication management plays a critical role in managing bipolar depression and requires careful consideration of various pharmaceutical approaches.
Medication Management for Bipolar Depression
Mood Stabilizers: The Foundation of Treatment
Mood stabilizers form the primary line of defense against bipolar depression. Lithium, a classic mood stabilizer, reduces suicidal thoughts and behaviors effectively. Lithium can lower suicide risk by approximately 80% in individuals with bipolar and other major affective disorders.

Valproic acid and lamotrigine are other commonly prescribed mood stabilizers, each with unique benefits and side effect profiles.
Antipsychotics: A Powerful Addition
Second-generation antipsychotics serve as valuable tools in managing bipolar depression. Drugs like quetiapine and lurasidone show significant efficacy in reducing depressive symptoms. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry found that quetiapine improved depressive symptoms in 58% of patients with bipolar depression (compared to 36% in the placebo group).
The Antidepressant Dilemma
Antidepressants require careful consideration in bipolar depression treatment. The risk of triggering manic episodes presents a significant concern. However, in some cases (particularly when combined with mood stabilizers), antidepressants can benefit patients. The key lies in close monitoring and individualized treatment plans.
Combination Therapies: Synergistic Effects
Combining medications often yields better results than monotherapy in managing bipolar depression. A study in the American Journal of Psychiatry found that the combination of olanzapine and fluoxetine proved more effective than either drug alone in treating bipolar depression. However, combination therapies also increase the risk of side effects, necessitating careful management and monitoring.
Pharmacogenetic Testing: Personalizing Treatment
Advanced pharmacogenetic testing optimizes medication selection. Genetic testing represents a significant advancement in personalized medicine for psychiatric care. This cutting-edge approach allows for tailored treatments based on an individual’s genetic makeup, potentially reducing trial and error in finding the most effective medication management regimen.
Medication management for bipolar depression requires expertise, careful monitoring, and a willingness to adjust strategies as needed. The next chapter will explore psychosocial interventions that complement medication management, providing a comprehensive approach to bipolar depression treatment.
Psychosocial Interventions for Bipolar Depression
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: Rewiring Thought Patterns
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) stands out as a highly effective psychosocial intervention for bipolar depression. This approach helps patients identify and challenge negative thought patterns, replacing them with more balanced and realistic perspectives. Studies show variable results in improving the level of depression and the severity of mania, improving functionality, and reducing relapses and recurrences in bipolar patients.
CBT techniques for bipolar depression often include:
- Mood monitoring to identify early warning signs of depressive episodes
- Activity scheduling to combat the tendency to withdraw during depressive periods
- Cognitive restructuring to address negative self-talk and catastrophic thinking
These strategies empower patients to take an active role in managing their condition, reducing the frequency and severity of depressive episodes.
Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy: Stabilizing Daily Routines
Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy (IPSRT) focuses on stabilizing daily routines and improving interpersonal relationships – two areas often disrupted in bipolar disorder. This approach recognizes the critical role of biological rhythms in mood regulation.
IPSRT helps patients:
- Establish consistent sleep-wake cycles
- Maintain regular meal times
- Balance work and leisure activities
- Improve communication in relationships
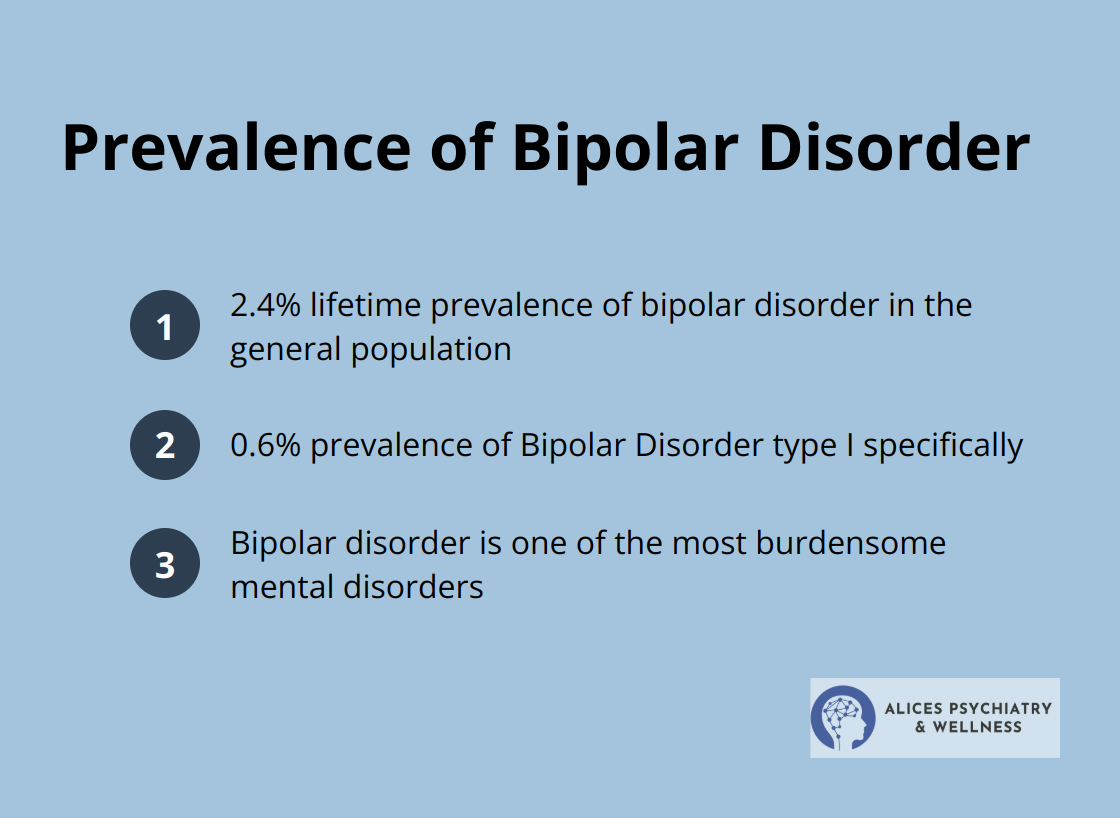
Bipolar disorder is one of the most burdensome mental disorders, with a lifetime prevalence of 2.4% and a prevalence of 0.6% for BD type I.
Family-Focused Therapy: Strengthening Support Systems
Family-Focused Therapy (FFT) recognizes the vital role that family members play in managing bipolar depression. This approach educates family members about the condition, improves communication, and enhances problem-solving skills within the family unit.
Key components of FFT include:
- Psychoeducation about bipolar disorder
- Communication enhancement training
- Problem-solving skills development
Research published in the Journal of Affective Disorders showed that patients receiving FFT in addition to pharmacotherapy had a 35% lower rate of relapse into depression over two years compared to those receiving standard care.
Group Therapy: Shared Experiences and Support
Group therapy provides a unique opportunity for individuals with bipolar depression to connect with others who share similar experiences. This form of therapy can reduce feelings of isolation and provide a platform for mutual support and learning.
Benefits of group therapy include:
- Increased social support
- Opportunities to learn from others’ experiences
- Practice of social skills in a safe environment
A study in the British Journal of Psychiatry found that group psychoeducation significantly reduced the number of depressive episodes in bipolar patients over a five-year follow-up period.
Final Thoughts
Effective management of bipolar depression requires a comprehensive, personalized approach that combines medication, psychosocial interventions, and ongoing support. Treatment bipolar depression guidelines emphasize the importance of continuous monitoring and adjustment as symptoms fluctuate and life circumstances change. Regular check-ins with mental health professionals allow for timely modifications to medication regimens and therapeutic approaches, ensuring optimal management of bipolar depression.
Patient education and self-management play vital roles in long-term success. Individuals who understand their condition can recognize early warning signs, implement coping strategies, and actively participate in their treatment. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of depressive episodes, improving overall quality of life.
The journey to manage bipolar depression continues, but with the right support and resources, individuals can achieve stability and lead fulfilling lives. At Alice’s Psychiatry and Wellness, we provide compassionate, expert care that addresses the unique needs of each patient (our personalized approach offers hope and practical solutions for those navigating the challenges of bipolar depression). Seeking help demonstrates strength, and with proper treatment and support, individuals with bipolar depression can thrive and achieve their personal goals.





